RhoGAM Half-Life
RhoGAM Has the Longest Half-Life of Any Anti-D Product1,2
-
RhoGAM1 (IM)
-
HyperRHO®3 (IM)
-
Rhophylac®4 (IM)
-
AABB Guidelines5
-
ACOG Guidelines6
Clinical effect of longer half-life has not been studied in head-to-head trials.
AABB = Association for the Advancement of Blood & Biotherapies | ACOG = American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists | IM = intramuscular
Not all anti-D brands are the same2
Why Half-Life Matters
Not all pregnancies are alike

The timing and amount of fetomaternal hemorrhage (FMH) is unpredictable and can present without clinical suspicion7,8

There is natural, individual variability in the anti-D half-life9

The concentration of anti-D circulating in the maternal bloodstream late in the third trimester varies for each pregnancy9

Longer half-life allows for greater residual anti-D in circulation over time10
It’s vital for patients to have sufficient anti-D levels circulating through delivery to reliably protect against Rh sensitization10,12,13
Half-Life StoryRhoGAM Protects Rh-Negative Mothers
Through Delivery
Risk of Rh sensitization is highest at delivery6,12,14
The 300 µg dose of anti-D in RhoGAM administered at 28 weeks is expected to ensure 20-30 µg of residual anti-D remains in maternal circulation at delivery9
With the longest half-life of 30.9 days, >12.5% (>37.5 µg) of anti-D could remain in circulation at week 401,2*
*No data, based on internal calculations. No head-to-head studies have compared the half-life or efficacy of all available anti-Ds.
RhoGAM helped set the standards and clinical practice guidelines that are still followed today6
How RhoGAM Works
RhoGAM is a passive Rh antibody that neutralizes any Rh-positive blood that has entered the mother’s circulation1
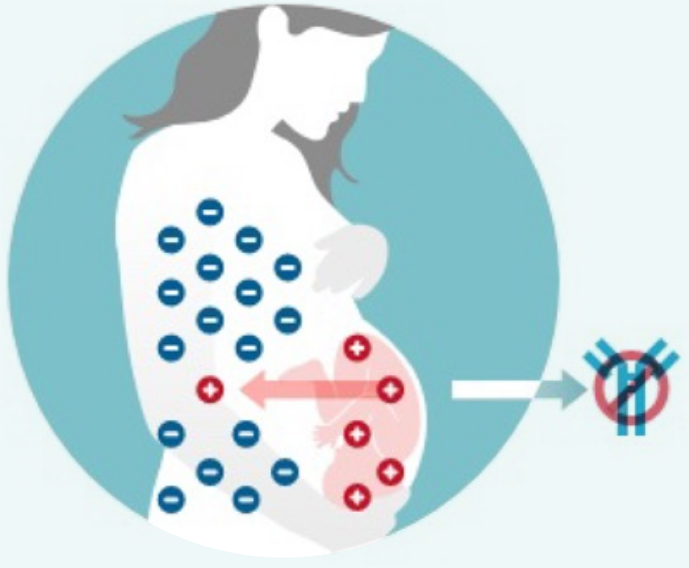
RhoGAM prevents the Rh-negative pregnant mother from making antibodies during pregnancy that could cause hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn (HDFN) in future pregnancies.1
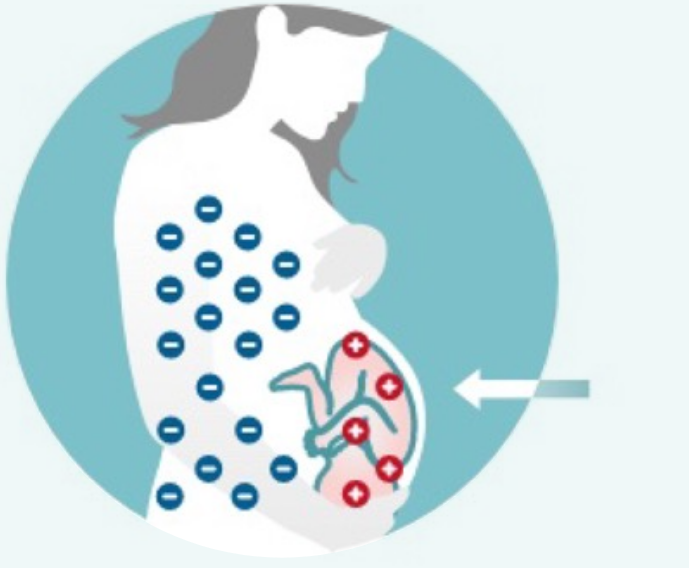
As long as the Rh-negative mother receives RhoGAM appropriately during every pregnancy, her babies are at very low risk of developing HDFN.1
The Impact of RhoGAM
Since the introduction of RhoGAM in 1968, the incidence of Rh sensitization has decreased dramatically10,12,13
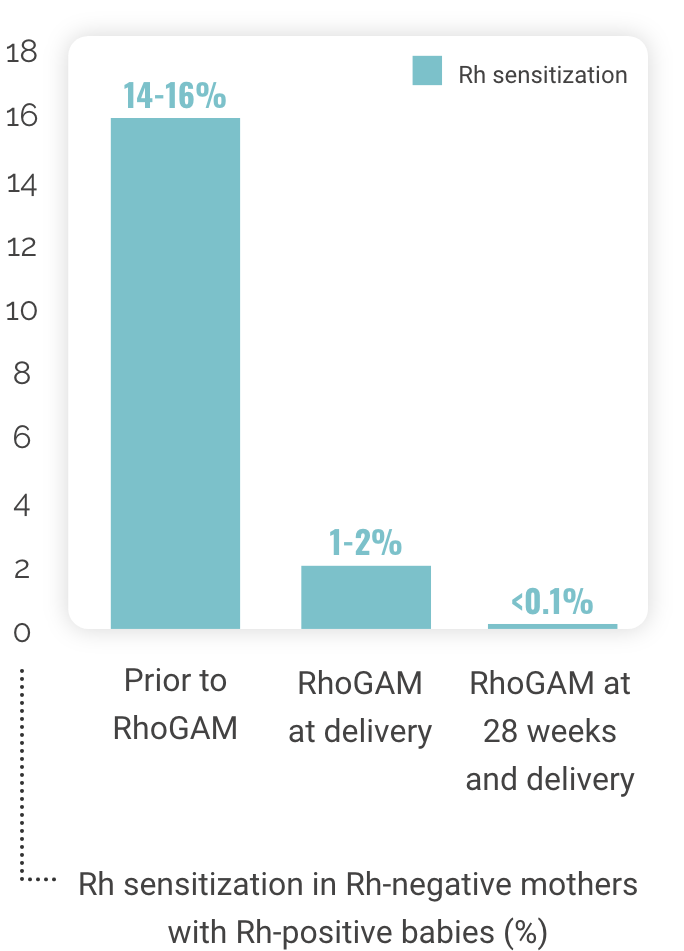
Rh sensitization in Rh-negative mothers
with Rh-positive babies (%)