Millions of life stories
begin with RhoGAM
Protecting Rh-negative mothers
through delivery1-3
The Irreplaceable Anti-D Prophylaxis
Only RhoGAM can be administered as early as 26 weeks to prevent Rh sensitization in Rh-negative pregnant mothers1
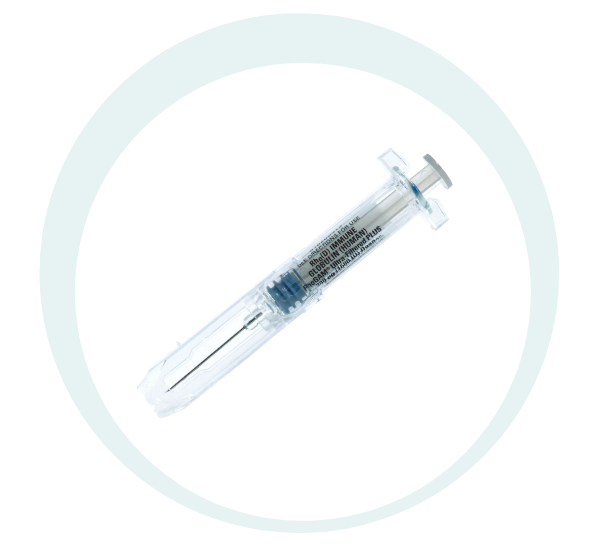
RhoGAM Ultra-Filtered PLUS [Rho(D) Immune Globulin (Human)] is a prescription medicine given by intramuscular injection that is used to prevent Rh sensitization in Rh-negative expectant mothers.1

RhoGAM may help protect your Rh-negative pregnant patients from Rh sensitization. During pregnancy, Rh sensitization of the mother may lead to hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn (HDFN) in future pregnancies.1
Manufacturing Update
We've taken steps to bolster RhoGAM production capabilities4:
Brought some manufacturing processes in-house to a Kedrion facility, expanding production capacity
Increased number of KEDPLASMA donation centers contributing to RhoGAM supply
Stock the Irreplaceable RhoGAM
How to OrderRhoGAM Remains the Trusted Standard
Throughout its over 50-year history, RhoGAM has incorporated innovations to remain the trusted standard in anti-D care1,4,5



- Percutaneous umbilical cord sampling (PUBS)
- Chorionic villus sampling (CVS)

Designed to offer protection from needlesticks by completely encompassing the needle once engaged.



Completed RhoGAM tech-transfer from Ortho-Clinical Diagnostics, Inc. to Kedrion manufacturing facility and opened 2 specialty plasma donation centers

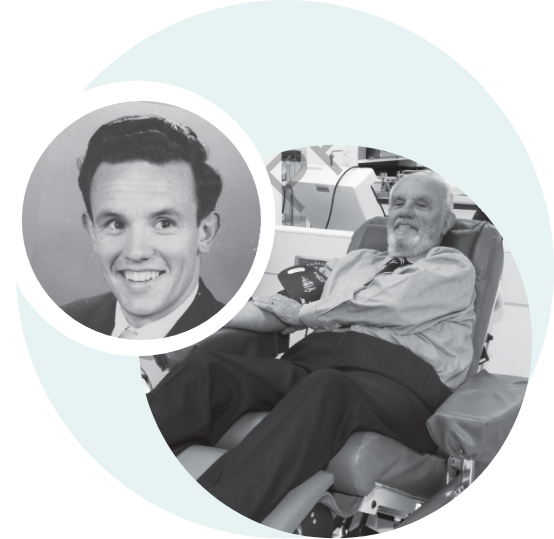
RhoGAM is the anti-D breakthrough that continues to make life-saving history4,6,7

The remarkable true story of one of the greatest medical breakthroughs of the 20th century.
Before the 1960s, there was no method available to prevent Rh immunization during Rh-incompatible pregnancies, which could result in hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn (HDFN).3 At that time, HDFN affected 9%-10% of all pregnancies and contributed significantly to fetal deaths in the US.8 Innovators were needed for this complex problem.
“Before it’s a breakthrough, it’s a crazy idea.”
A team of scientists were convinced that the answer could be what was then an unconventional theory. Known as passive antibody immunosuppression, an active immune response is prevented by passive administration of antibodies directed to the stimulus.9-11 Based on this idea, it was theorized that administering passively administered anti-D immunoglobulin to Rh-negative mothers could help prevent Rh immunization.

“A story of heroism and triumph. Of brilliant science and generous empathy.”
Before the 1960s, employing passive antibody immunosuppression to garner an immune response was not well received. But the research team remained dedicated to this idea to reduce Rh-sensitivity. As a result, in 1968, the FDA approved the use of RhoGAM to help prevent Rh immunization.1 As the first anti-D product available, RhoGAM has given hope to Rh-negative mothers by protecting millions of Rh-positive babies for five decades.2,4,6,7